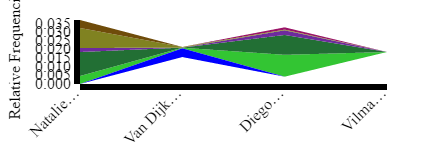
| undefined |
the four dimensions associated with |
exclusion |
are not evenly manifest throughout |
| undefined |
the capital” (Chancellor, Colombia). Another |
exclusion |
factor that affects university institutions |
| undefined |
financial difficulties are also an |
exclusion |
factor. Thus, young people from |
| undefined |
of the governing boards regarding |
exclusion |
factors for young people from |
| undefined |
approach, we must consider that |
exclusion |
is a contextual factor that |
| undefined |
by HEIs to prevent the |
exclusion |
of vulnerable students must be |
| undefined |
guidelines for dealing with the |
exclusion |
of vulnerable students. In this |
| undefined |
constitute critical dimensions of social |
exclusion |
(Byrne, 2005). Recent
research (Mato |
| undefined |
combating the
permanent nature of |
exclusion |
(Chowdry, Crawford, Dearden, Goodman, & Vignoles |
| undefined |
at risk or in social |
exclusion |
(Marquez
et al., 2007). Bashir |
| undefined |
it. Identifying
these factors of |
exclusion |
allows us to take decisions |
| undefined |
are factors that can generate |
exclusion |
among young people: When there |
| undefined |
it is advisable to adapt |
exclusion |
analysis criteria
to the political |
| undefined |
exclusion from university, and how |
exclusion |
becomes apparent
in the progression |
| undefined |
Although, as we have mentioned, |
exclusion |
can manifest itself in different |
| undefined |
invest financial resources is another |
exclusion |
factor. Poverty
and access to |
| undefined |
participants of the topic analyzed: |
exclusion |
factors
in Latin American higher |
| undefined |
seven
participants each. Considering that |
exclusion |
factors are affected by contextual |
| undefined |
related perspective
requires rethinking the |
exclusion |
factors described above, as their |
| undefined |
obtained allow us to classify |
exclusion |
factors for vulnerable groups in |
| undefined |
an empirical analysis of students’ |
exclusion |
factors from risk environments
to |
| undefined |
depth governing
board perceptions about |
exclusion |
factors in HEIs in Latin |
| undefined |
university governing boards’
viewpoints on |
exclusion |
factors in Latin American higher |
| undefined |
transition). The intrinsic
dimension includes |
exclusion |
factors linked to personal characteristics |
| undefined |
initiatives and
actions to minimize |
exclusion |
factors. This view was expressed |
| undefined |
The extrinsic elements that explain |
exclusion |
from HEIs include the factors |
| undefined |
factors generating
disadvantage, forms of |
exclusion |
from university, and how exclusion |
| undefined |
Identifying the factors that generate |
exclusion |
in higher
education is essential |
| undefined |
identified five factors that explain |
exclusion |
in higher
education: (a) personal |
| undefined |
Hernández, 2008), reducing inequalities and |
exclusion |
in Latin America, as
a |
| undefined |
establish mechanisms to avoid
the |
exclusion |
of people belonging to the |
| undefined |
eradicating the permanent marginalization
and |
exclusion |
of the most vulnerable groups |
| undefined |
about institutional policies
to reduce |
exclusion |
of the most vulnerable students |
| undefined |
both
to understanding the inclusion– |
exclusion |
phenomenon in higher education and |
| undefined |
also become a factor of |
exclusion |
, although this also depends
on |
| undefined |
for groups at risk of |
exclusion |
, ignoring
priority groups, not recognizing |
| undefined |
to students at risk of |
exclusion |
, particularly the role of teaching |
| undefined |
the most part, exposed to |
exclusion |
, poverty, and the effects of |
| undefined |
become a key factor in |
exclusion |
. In fact, the close connection |
| undefined |
present a higher risk of |
exclusion |
. This circumstance is more apparent |
| undefined |
2010). Prior research on binomial |
exclusion |
/inclusion
and inequalities in higher |
| undefined |
to minimize the risk of |
exclusion |
:
238 Education and Urban Society |
| undefined |
people’s situations of vulnerability or |
exclusion |
:
I don’t believe we have |